
Shipping between neighboring countries, Chile and Peru, has grown in importance, thanks to strong economic ties and free trade agreements. Whether you are a freight forwarding company, logistics provider, importer, exporter, customs broker, manufacturer, or an e-commerce business, understanding the nuances of cross-border shipping between these two Latin American countries is vital to ensuring smooth operations.
This comprehensive guide will take you through the essential considerations, challenges, regulations, and best practices when shipping goods from Chile to Peru.
Overview of Chile-Peru Trade Relations
Bilateral Trade Agreements
Chile and Peru enjoy a robust trading relationship, backed by various bilateral and multilateral trade agreements. One of the key pacts is the Pacific Alliance, which includes Chile, Peru, Colombia, and Mexico. This agreement eliminates most tariffs on goods traded between these countries, making shipping more cost-effective for businesses.
The Chile-Peru Free Trade Agreement (FTA), signed in 2006, also reduces trade barriers and promotes economic cooperation between both nations. More than 90% of goods traded between the two countries benefit from tariff-free movement, making it an ideal route for manufacturers, producers, and logistics companies looking to expand in the region.
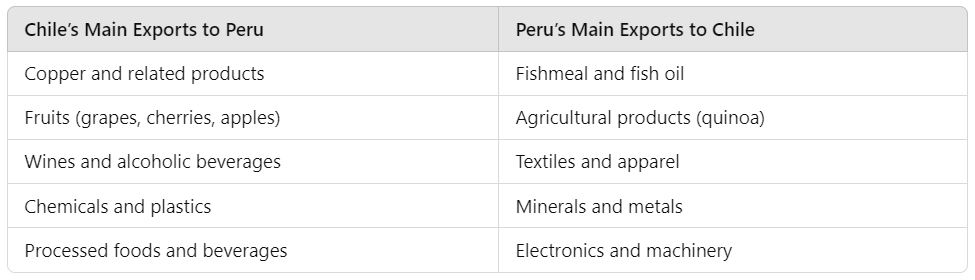
Key Exports and Imports
Understanding the type of goods frequently exchanged between Chile and Peru can help freight forwarders and logistics providers anticipate the shipping requirements for certain products.
The Growing Logistics Market
The trade between Chile and Peru has seen an upward trend, driven by both nations’ efforts to diversify their exports and imports. Given the strategic location of Peru as a gateway to the broader Andean region and Chile’s competitive advantages in raw materials, logistics providers, customs brokers, and freight forwarders have much to gain by tapping into this vibrant shipping market.
 Modes of Shipping Between Chile and Peru
Modes of Shipping Between Chile and Peru
Shipping goods from Chile to Peru offers several transportation options, each suited to different types of cargo, delivery timelines, and cost considerations.
1. Road Freight
One of the most common modes of transport for shipping between Chile and Peru is road freight. This option is particularly appealing for cross-border trade, as both countries share a 160-kilometer border. The Pan-American Highway connects both nations, allowing trucks to transport goods relatively quickly.
Key Advantages:
- Cost-effective: Road transport is generally less expensive compared to air freight and ideal for bulk cargo.
- Flexible: It offers flexibility in terms of loading and unloading points, making it suitable for small and medium businesses.
- Reduced Handling: Goods can often travel from warehouse to warehouse without the need for transshipment, reducing the risk of damage.
Considerations:
- Transit Time: While quicker than ocean freight, road transport can still take several days, depending on the starting and ending points.
- Border Procedures: Cross-border transport can involve customs clearance, documentation, and inspection at the border, which may delay shipments.
2. Ocean Freight
For large volumes of goods, particularly bulk and containerized cargo, ocean freight is a cost-effective solution. Chile’s key ports, such as Valparaíso and San Antonio, have regular services to Peru’s largest ports, including Callao and Paita.
Key Advantages:
- Cost Savings: Ocean freight is ideal for transporting high volumes of goods at a relatively low cost.
- Sustainability: Shipping by sea is more environmentally friendly than air freight, making it attractive for companies prioritizing sustainability.
- Specialized Cargo: Ocean freight can accommodate a wide range of goods, including perishables, hazardous materials, and oversized equipment.
Considerations:
- Longer Transit Times: Shipping by sea is slower, taking 5-10 days, depending on the shipping route and weather conditions.
- Port Congestion: Some ports, especially in Callao, may experience congestion during peak seasons, which can delay delivery schedules.
3. Air Freight
For time-sensitive shipments, air freight is the fastest option. Major airlines operate between Chile’s Arturo Merino Benítez International Airport (SCL) and Peru’s Jorge Chávez International Airport (LIM), enabling quick transport of goods.
Key Advantages:
- Fast Delivery: Air freight is the best option for urgent shipments, often taking just 1-2 days.
- Security: Air cargo is generally less susceptible to theft and damage due to tight security controls.
- Ideal for High-Value Goods: Air freight is suitable for shipping high-value, lightweight, or perishable goods like electronics, pharmaceuticals, and fresh produce.
Considerations:
- Higher Costs: Air freight is significantly more expensive than road or ocean transport, making it less viable for large or low-margin shipments.
- Limited Cargo Capacity: Airplanes have strict weight and size limitations, meaning bulky items may need alternative transportation methods.
 Key Documentation for Shipping From Chile to Peru
Key Documentation for Shipping From Chile to Peru
To ensure smooth customs clearance and avoid delays, accurate documentation is critical when shipping goods from Chile to Peru. Below are the key documents required:
- Commercial Invoice: A document that outlines the details of the transaction, including the buyer, seller, description of goods, value, and terms of sale.
- Bill of Lading (B/L) or Air Waybill (AWB): This document serves as a receipt of the cargo and contract for its transport. It is provided by the freight carrier.
- Packing List: A detailed list that describes the contents of the shipment, including weight, dimensions, and packaging details.
- Certificate of Origin: For goods benefiting from preferential tariff treatment under the Chile-Peru FTA, this document proves the origin of the goods.
- Insurance Certificate: Provides proof of insurance coverage for the shipment.
- Import and Export Permits: Some goods, such as hazardous materials, require additional permits or licenses to enter or exit the country.
- Customs Declaration: Submitted to customs authorities, this document details the shipment for taxation and regulatory purposes.
Customs Regulations Between Chile and Peru
Navigating customs can be a challenge for logistics providers, freight forwarders, importers, and exporters. It is crucial to understand the customs regulations to ensure compliance and minimize delays.
Tariffs and Duties
Due to the Chile-Peru FTA, most products shipped between the two countries enjoy duty-free treatment. However, some goods may still be subject to tariffs depending on their classification under the Harmonized System (HS) codes. Customs brokers can assist with determining the correct HS code for goods to ensure compliance with both Chilean and Peruvian customs regulations.
VAT and Import Taxes
In addition to tariffs, shipments may be subject to Value-Added Tax (VAT) and other local taxes upon entry into Peru. Peru’s VAT rate is 18%, and it applies to both imported goods and services. Importers should account for this tax in their total landed cost to avoid surprises.
Inspection and Clearance
Customs inspections can be required based on the type of goods being imported. For example, agricultural products, chemicals, and hazardous materials may need additional inspections to ensure compliance with health, safety, and environmental regulations. Importers and logistics providers should be prepared for possible delays in clearing such goods through customs.
Challenges in Shipping From Chile to Peru
Despite the advantages of shipping between Chile and Peru, there are also challenges to consider.
1. Border Delays
While the Pan-American Highway facilitates overland shipping, customs checkpoints at the border can cause delays. These delays may be due to heavy traffic, documentation errors, or extended inspections. Freight forwarders should account for potential delays in their scheduling.
2. Port Congestion
Ports such as Callao in Peru often experience congestion during peak seasons, particularly around major holidays and the end of the fiscal year. This congestion can lead to longer waiting times for vessels, causing delays in the delivery schedule. Shipping companies should consider alternative ports or routes if possible to mitigate congestion risks.
3. Weather Conditions
Both Chile and Peru are prone to adverse weather conditions that can disrupt shipping schedules. For example, the coastal areas of Peru are frequently affected by fog, while Chile may experience storms that disrupt maritime transport. Logistics providers should monitor weather patterns and have contingency plans in place.
4. Regulatory Changes
Regulatory changes in either country can impact shipping operations. Both Chile and Peru periodically revise their import-export laws, taxes, and customs procedures. Staying updated on these changes is crucial for maintaining compliance and avoiding penalties.
Best Practices for Shipping From Chile to Peru
1. Work With a Reputable Freight Forwarder
Choosing an experienced freight forwarder or logistics provider can make all the difference when shipping from Chile to Peru. They can handle everything from route planning to customs clearance, ensuring your goods are delivered on time and without issues.
2. Optimize Packaging
Proper packaging is essential to protect goods in transit and minimize shipping costs. Using the right type of packaging, especially for fragile or perishable items, will reduce the risk of damage and ensure that the goods arrive in good condition.
3. Plan for Customs Clearance
Understanding the customs regulations of both Chile and Peru is critical. Work with customs brokers who can ensure that all necessary documentation is prepared and submitted correctly to avoid delays at the border or port.
4. Consider Insurance
While many companies try to cut costs by skipping cargo insurance, it is a critical safety net for international shipments. Insurance protects your goods against loss or damage during transit, giving you peace of mind throughout the shipping process.
5. Stay Informed on Trade Agreements
Freight forwarders, customs brokers, and importers/exporters should stay updated on any changes to trade agreements between Chile and Peru. These agreements can significantly impact tariffs, documentation, and shipping costs.
 Conclusion
Conclusion
Shipping from Chile to Peru offers a wealth of opportunities for businesses across various industries. The strong trade relations between the two countries, coupled with free trade agreements and efficient transportation routes, make it a promising market for logistics providers, freight forwarders, customs brokers, manufacturers, and e-commerce businesses. By understanding the logistics, regulations, and challenges involved, companies can optimize their supply chains and ensure seamless cross-border transactions.
From choosing the best shipping method to ensuring compliance with customs regulations, navigating the Chile-Peru shipping lane can be complex but highly rewarding with the right strategies in place.



 Modes of Shipping Between Chile and Peru
Modes of Shipping Between Chile and Peru Key Documentation for Shipping From Chile to Peru
Key Documentation for Shipping From Chile to Peru Conclusion
Conclusion



